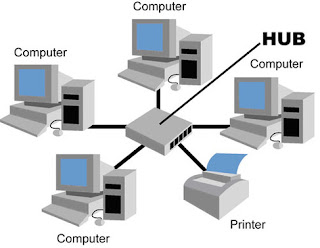
What are the Types of Cable
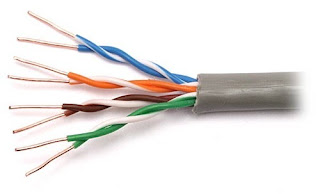
Twisted Pair - A twisted pair cable is a type of cable made by putting two separate insulated wires together in a twisted pattern and running them parallel to each other. This type of cable is widely used in different kinds of data and voice infrastructures. Experts point out that twisted pair cabling is often used to help avoid certain kinds of signal interference. Two different types of twisted pair cable, unshielded twisted pair (UTP) and shielded twisted pair (STP) are used in different kinds of installations. UTP is common in Ethernet installations, while STP is used in various kinds of networks to prevent cross talk and electromagnetic interference. STP cable can also help to provide grounding. In general, twisted-pair cabling may be preferred over a common alternative, coaxial cable, for different reasons. Coaxial cable involves a single, thicker wire. Many of those who use this type of cable claim that twisted pair has a more...